
An Agile Framework for Research and Development
Joseph Mariña Innovation at LMI, Human Centered Design, AgileA quick search of "Agile for research and development" makes two things clear:
- Research and development (R&D) processes need agility beyond the software development space.
- Companies struggle to match agile frameworks to their R&D needs.
As LMI generated an operating model to develop prototypes around innovative and crowdsourced ideas in short timelines (30–45 days), the difficulty became apparent. While LMI has mature teams practicing scrum, Kanban, extreme programming (XP), and the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), the compressed timelines and enhanced uncertainty around scope and technology presented unique challenges requiring a new approach. This method (shown in Figure 1) expressly supports the development of rapid prototypes where scope and technology are initially undefined. Why does R&D need something different?
- The open-ended definition of “done” for exploratory efforts clashes with sprint planning (scrum).
- Reaching an endpoint in a timebox is a challenge for Kanban.
- Shortened timelines devalue estimation while augmenting demand for shorter feedback loops.
- Abridged timelines mean that overhead with iteration management needs to be kept tight.

Focusing on the Right Things
To support these efforts LMI developed Ranger™ – a deconstructed agile framework. Framework development must start with goals and principles. Inculcating a team with unified purpose creates alignment and offers team members a beacon when facing an uncertain situation. Standards and principles drive our practices and tools. With each prototype kickoff, we reintroduce our mission and core values.
Our mission is to prove the concept. We aim to establish or demonstrate feasibility, not implement the concept perfectly. We do this through the following core values:
- Creating and preserving momentum
- Practicing ruthless prioritization and ignoring sunk costs
- Emphasizing positioning over planning.
With our mission in mind, the team decided which practices and roles to introduce, alter, and keep from various agile frameworks.
Designing Agile Practices Around Core Values
Ranger™ has similarities to scrum, Kanban, and the dynamic systems development method. However, significant changes and small adjustments make this process unique.
The Significant Changes
Most agile practices use consistent iteration lengths of 2–4 weeks. When working on a 30- or 45-day prototype, this period represents an unacceptable timeline for feedback. Compressed project lengths make capacity measures, like story points, relatively useless (it takes about three iterations to calculate velocity). Ranger™ solves this issue by creating variable-length iterations, called orbits. An orbit lasts 2–5 business days and is goal-focused. The team agrees to the length at each orbit start, based on the goal. Setting a short orbit helps the team right-size goals while variable orbit sizes enable the team to swarm around the true objective without adding filler to round out capacity. When reflecting on our core values, varying length iterations consistently helped our teams create momentum, prioritize ruthlessly, and emphasize positioning.
The other significant adjustment was around roles. Prototype idea generators and subject matter experts often have other commitments preventing them from working as a product owner. We formalized the roles of innovators and sponsors for unique contributions to the prototype vision.
- The innovator has the idea or vision of what a fully developed product can be.
- Market and service line sponsors have insights into proposals and clients that could benefit from the prototype outcome in the near term.
- The product owner defines an achievable prototype scope that marries these insights.
Splitting these responsibilities across technical, business, and functional experts generates a healthy friction. Introducing and sharing multiple vantage points promotes broader education around the problem and how the prototype fits into that narrative.
The Small Adjustments
Although, like with other agile frameworks, teams perform daily stand-ups, iteration reviews, and practice continuous improvement through retrospectives, these ceremonies underwent minor adjustments to account for our context. For example, we have a single formal retrospective at about the 1/3 mark of the prototype and a post-mortem retrospective at its conclusion. This timeline ensures improvement and reflection while preserving momentum and reducing overhead. Figure 2 shows how these ceremonies fit in the framework.
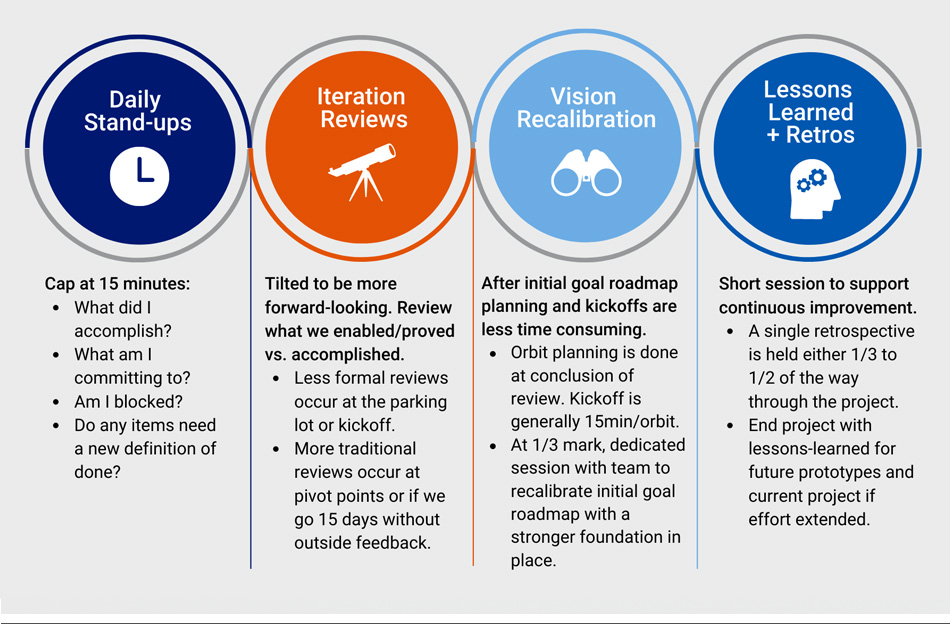
The Results
In one year, 16 prototypes reached completion using the Ranger™ framework. While not every prototype receives further funding for product development, each furnishes enough information for an educated decision regarding further investment. All prototypes have achieved that objective, with a representative proof of concept delivered on time to support decision-making.
Several of the most successful prototypes had significant pivots or concluded with a scope outside of the initial plan, outlining the need for constant positioning based on discoveries and overall agility. Understanding a problem and proving the capacity to solve it in these timeframes has implications for the government’s acquisition and proposal process and can increase confidence in how the government approaches complex problems.
While existing methods might not fit perfectly in every context, adaptations and custom frameworks can bring agility to non-traditional use cases.

Joseph Mariña
Fellow, Agile Transformation CoachJoseph Mariña has experience as a scrum master and agile coach across many agile frameworks. He has more than ten years of experience working on an array of technical solutions.



